Merkel Cell Carcinoma Immunohistochemistry
These can lead to diagnostic difficulty. 4 Cheuk W et al.

An Update On Diagnostic Features Of Merkel Cell Carcinoma Diagnostic Histopathology
Merkel cell carcinoma immunohistochemistry polyoma virus CAM 52 INTRODUCTION Merkel cell carcinoma MCC is an aggressive tumor that often develops on sun exposed skin as a firm flesh colored nodule1 Tumors are often non-descript and clinicians often consider other more common skin tumors in the differential diagnosis.

Merkel cell carcinoma immunohistochemistry. Recently cytogenetic analysis has emerged as a potential tool in the diagnosis of solid neoplasms including MCC. 1 Currently a multidisciplinary approach to treatment is recommended consisting of wide local excision of the primary tumor. Histologically tumor cells which extended from the dermis into the subcutis showed anastomosing bands with partial trabecular pattern.
Some of the genes are potential therapeutic targets. Adhikari LA1 McCalmont TH Folpe AL. Immunohistochemistry is often used to confirm Merkel cell carcinoma MCC.
Immunostaining for thyroid transcription factor-1 and cytokeratin 20 aids in the distinction of small cell carcinoma from Merkel cell carcinoma but not. We built a tissue microarray with 162 trichoepithelioma and 328 basal cell carcinoma biopsies and. 1Department of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology Mayo Clinic Rochester MN 55905 USA.
Basal cell carcinoma showing the Bcl-2 immunostaining of the. Merkel cell tumors stain positively for NSE as would any APUD cell tumor. Immunohistochemical and ultrastructural analyses are usually helpful in differentiating these neoplasms.
Results Ten of 11 MCCs stained with the antibody to CK20. The authors investigated cytokeratins CKs 56 7 17 and 20 staining in paraffin sections of 26 Merkel cell carcinomas to expand the knowledge of the CK staining profile of this entity. They also demonstrate perinuclear staining.
The literature suggests that p63 expression in Merkel cell carcinoma MCC is associated with a poor prognosis. Agnosis frequently requires support by immunohistochemistry. P63 immunohistochemistry marks the 2 main isoforms of this transcriptional protein.
Cytokeratin 20 CK20 positivity is currently used to distinguish. Two cases of Merkel cell carcinoma MCC were examined by electron microscopy and immunohistochemistry. The literature records many examples of Merkel cell carcinoma MCC exhibiting aberrant immunohistochemical profiles.
Merkel cell carcinoma a rare cutaneous neuroendocrine tumor of the skin can be categorized into two groups according to Merkel cell polyomavirus MCV presence. Aim To investigate whether immunohistochemical staining for cytokeratin 20 CK20 and thyroid transcription factor 1 TTF-1 is useful in distinguishing Merkel cell carcinomas MCCs from metastatic small cell carcinomas SCCs. Diagnosis requires microscopic evaluation as the clinical appearance is nonspecific and can mimic a variety of benign and malignant skin lesions.
Merkel cell carcinoma MCC is a cutaneous neoplasm histopathologically difficult to differentiate from other small blue cell neoplasms. MCV-negative tumors are more aggressive and frequently associated with gene mutations. Merkel cell carcinoma is a highly aggressive primary cutaneous neuroendocrine carcinoma primarily affecting elderly and immunosuppressed individuals.
ALK and EGFR expression by immunohistochemistry are associated with Merkel cell polyomavirus status in Merkel cell carcinoma Tuukka Veija Mia Kero Virve Koljonen Tom Böhling Department of Pathology. Merkel cell carcinoma with heterologous rhabdomyoblastic differentiation. Merkel cell carcinoma is a rare neuroendocrine carcinoma of the skin mostly induced by Merkel cell polyomavirus integration.
Merkel cell carcinoma is an aggressive tumour that usually arises on chronically sun exposed skin of the elderly. They also demonstrate perinuclear staining with antikeratin antibodies to low-molecular-weight cytokeratins 8 18 and 19. TAp63 tumor suppressorlike properties and Np63 oncogenic properties.
Immunohistochemistry for Merkel cell polyomavirus is highly specific but not sensitive for the diagnosis of Merkel cell carcinoma in the Australian population Author links open overlay panel Julie Y. Merkel cell tumors stain positively for NSE as would any APUD cell tumor. Methods Eleven cases of MCC and 10 of lung SCC were stained for CK20 and TTF-1.
Gill FRCPA a e. Ultraviolet radiation immunosuppression and the Merkel cell polyomavirus MCPyV are thought to be causative factorsThe cell of origin remains debatable but the immunohistochemical profile and morphology resemble native Merkel cells in the skin. All three CK 20negative tumors showed punctate staining.
1 Its metastatic potential has been compared with that of melanoma with an even higher mortality rate than the latter. The ultrastructural study showed tumor cells in case 1 with numerous neurosecretory granules. The role of immunohistochemistry for Merkel cell polyomavirus large T-antigen in confirmation.
Reactivity with anti-CK 20 was demonstrated in 23 of 26 Merkel cell carcinomas 88. Immunohistochemistry is often used to confirm Merkel cell carcinoma MCC. Merkel cells are absent in.
Merkel cell carcinoma MCC is a rare but highly aggressive cutaneous malignancy that principally occurs on the sun-exposed areas of older white men. Paik MBBS a Geoffrey Hall FRCPA b Adele Clarkson BSc a Lianne Lee MBBS c Christopher Toon MBBS d Andrew Colebatch MBBS a Angela Chou FRCPA c Anthony J. The number of granules in case 2 however was smaller.
Merkel cell carcinoma of the skin primary neuroendocrine cell carcinoma of the skin Clinical features Typically a rapidly growing lesion on sun-damaged skin of the head and neck or extremities of the elderly 10Clinical diagnoses are commonly erroneous. The objectives of the current study were 1 to examine the immunohistochemical profile of different subsets of MCC to determine whether pred.

Clinical Features And Outcomes Of Merkel Cell Carcinoma In 20 Cats Sumi 2018 Veterinary And Comparative Oncology Wiley Online Library

Pathology Outlines Merkel Cell Carcinoma

Immunohistochemistry Of Merkel Cell Carcinoma Metastases 400 Original Download Scientific Diagram
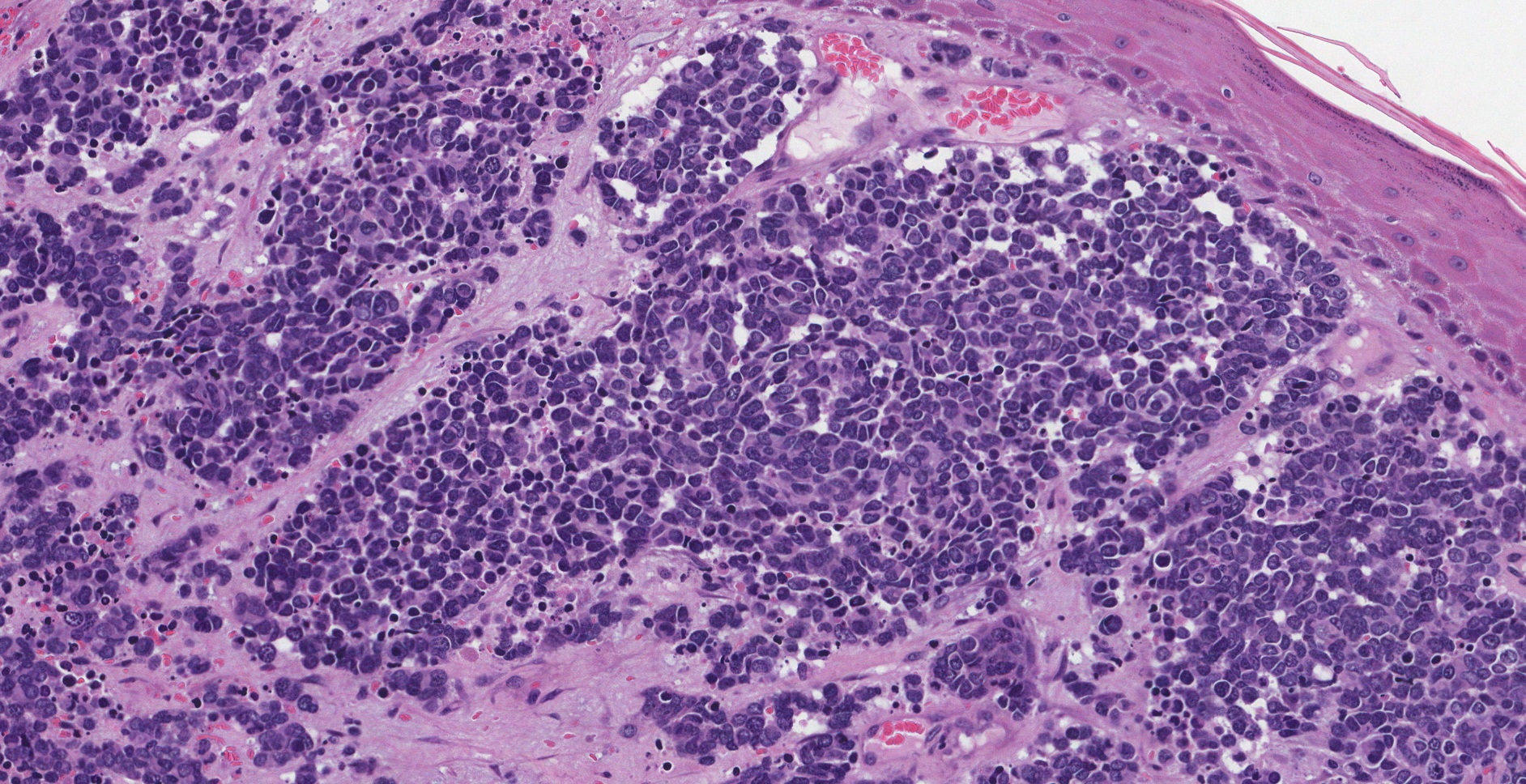
Merkel Cell Carcinoma Mypathologyreport Ca
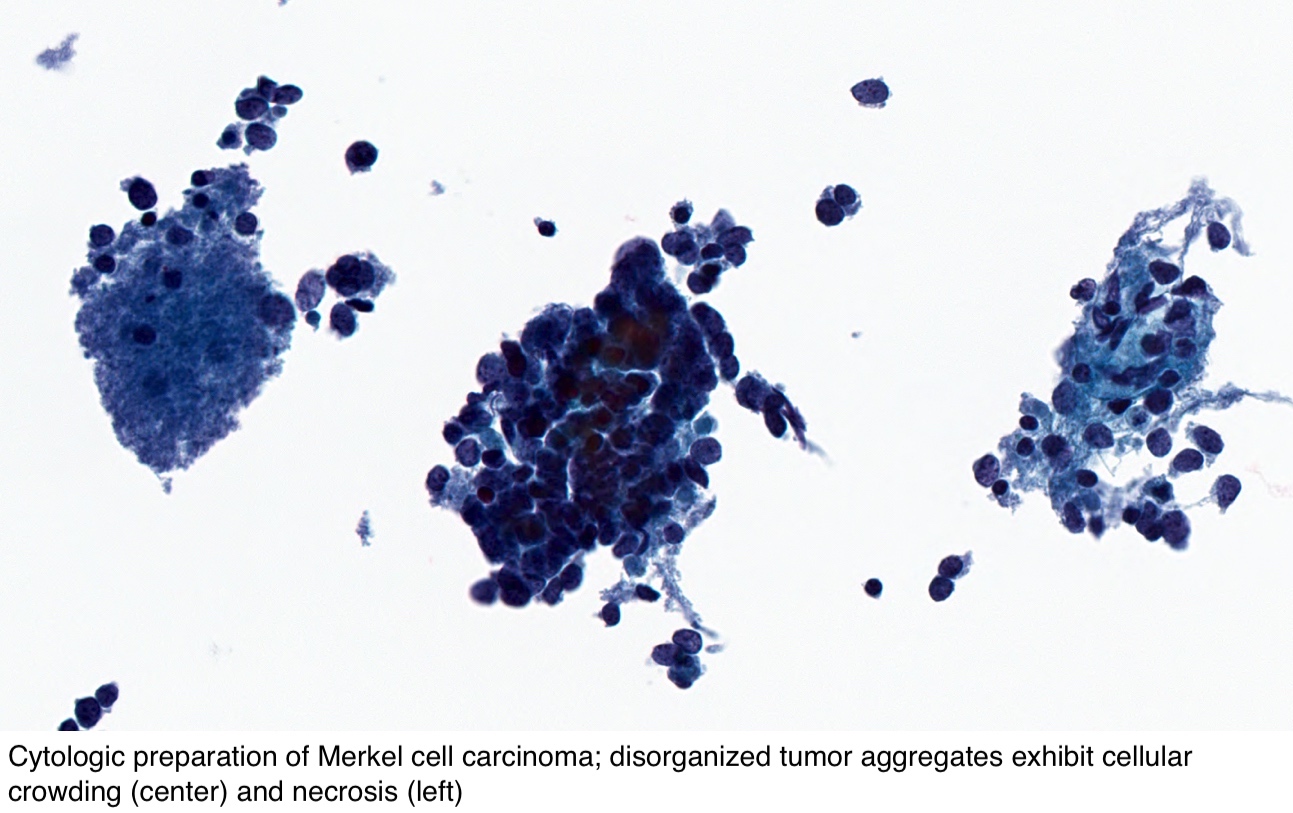
Pathology Outlines Merkel Cell Carcinoma
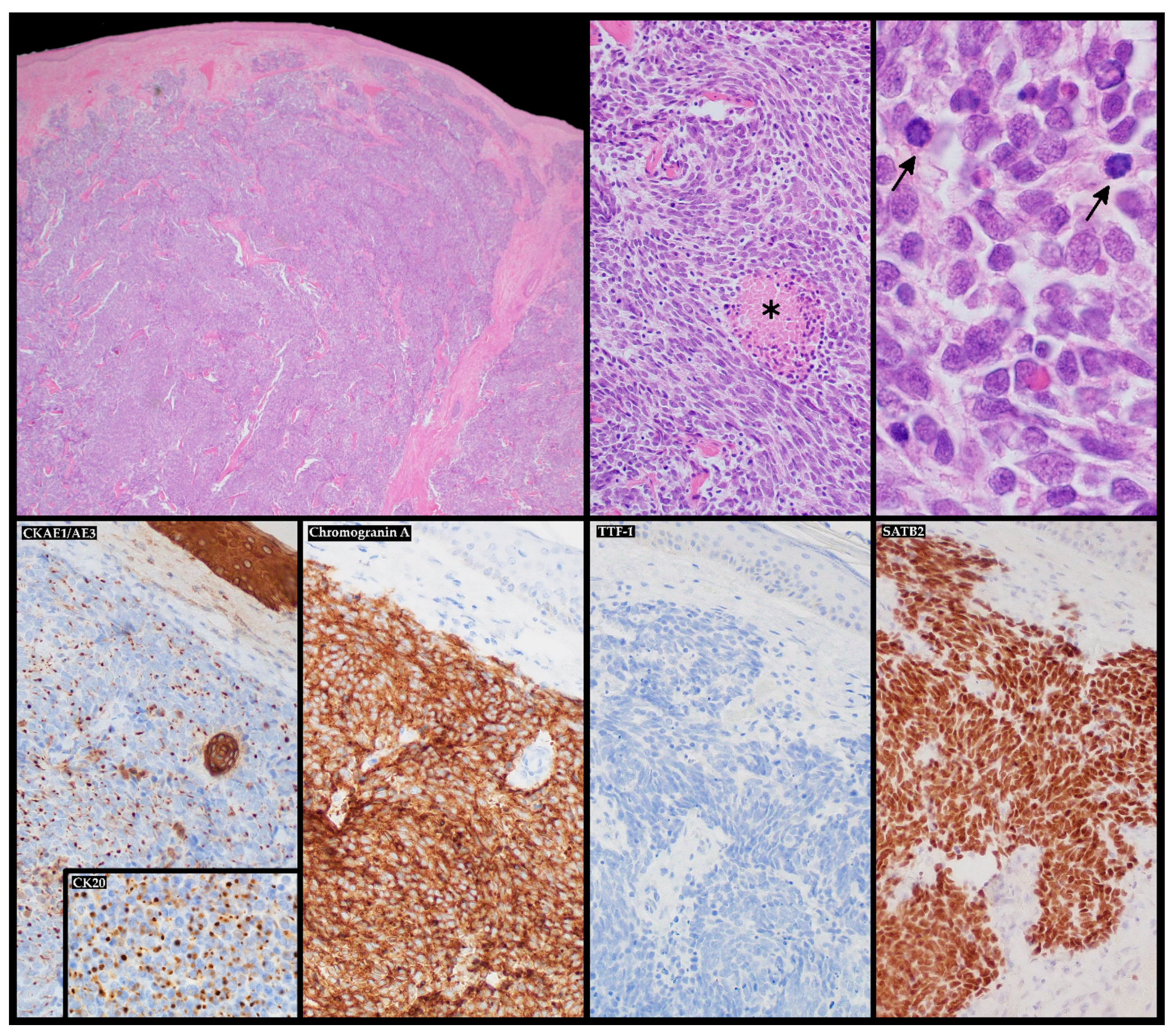
Ijms Free Full Text Merkel Cell Carcinoma From Molecular Pathology To Novel Therapies
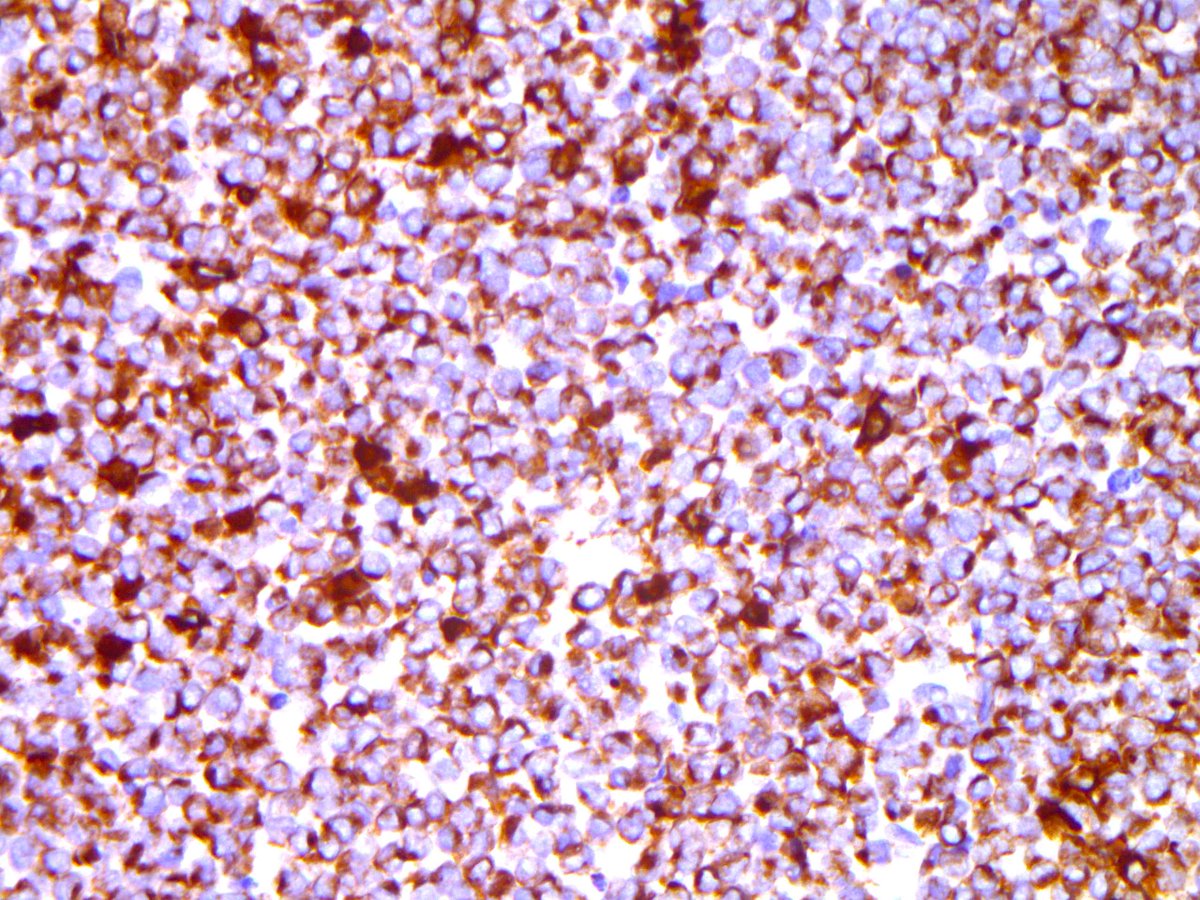
Brendan Dickson Md On Twitter Merkel Cell Carcinoma Ihc Ck20 Chromogranin Nb Sheets And Nodules Of Basophilic Cells Granular Chromatin
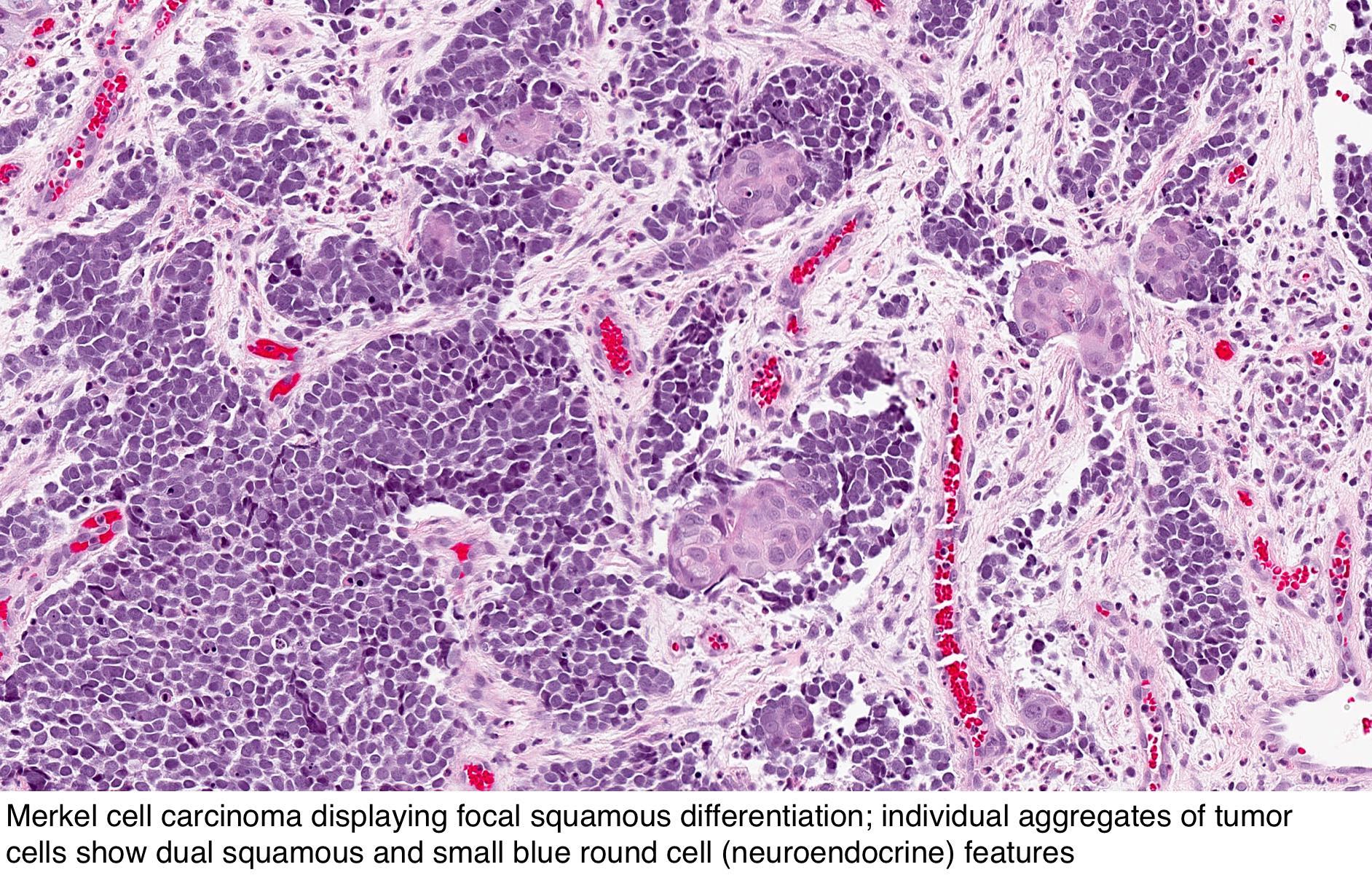
Pathology Outlines Merkel Cell Carcinoma
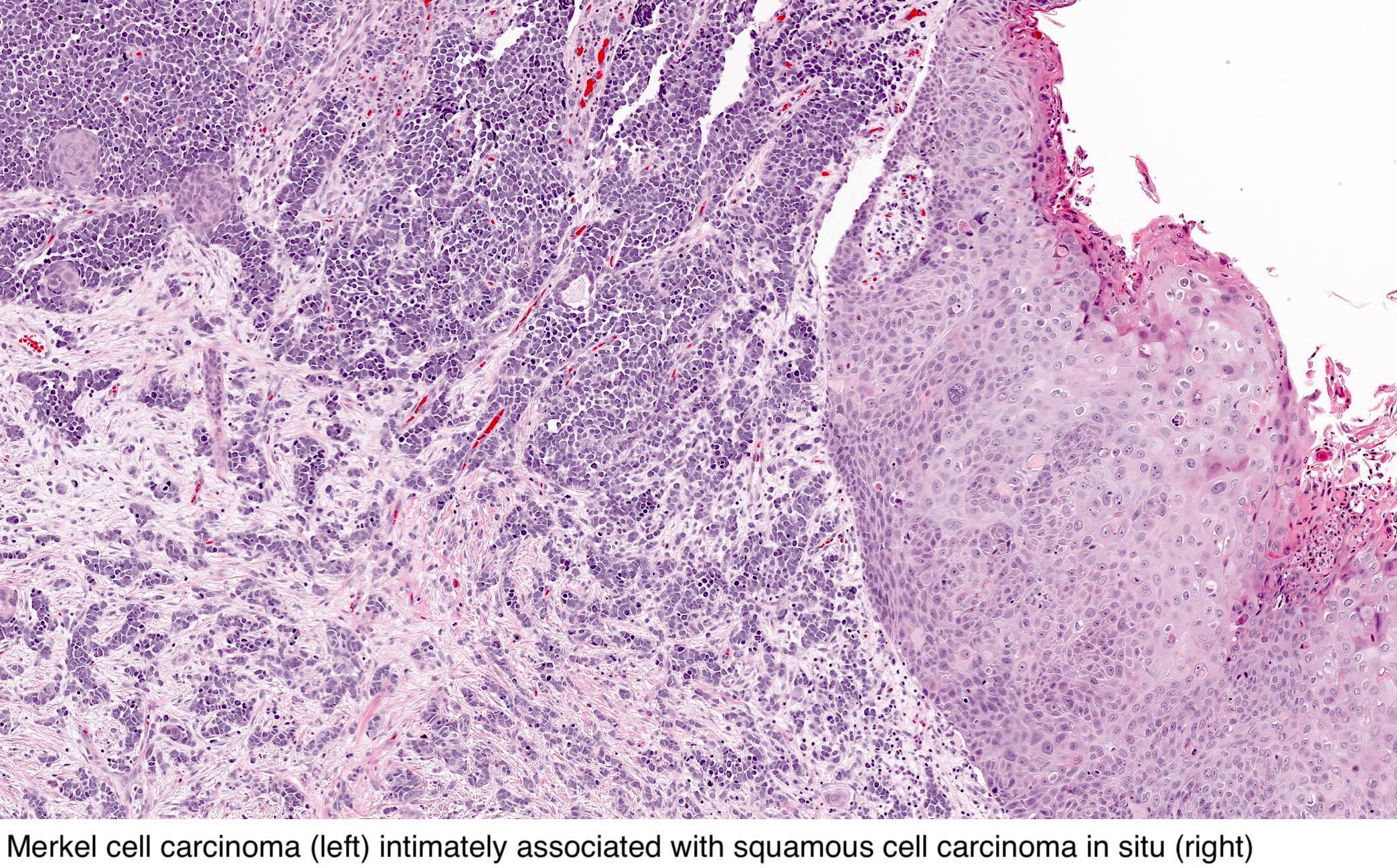
Pathology Outlines Merkel Cell Carcinoma

Merkel Cell Carcinoma Can Be Distinguished From Metastatic Small Cell Carcinoma Using Antibodies To Cytokeratin 20 And Thyroid Transcription Factor 1 Journal Of Clinical Pathology

Immunohistochemistry Of Merkel Cell Carcinoma Metastases 400 Original Download Scientific Diagram

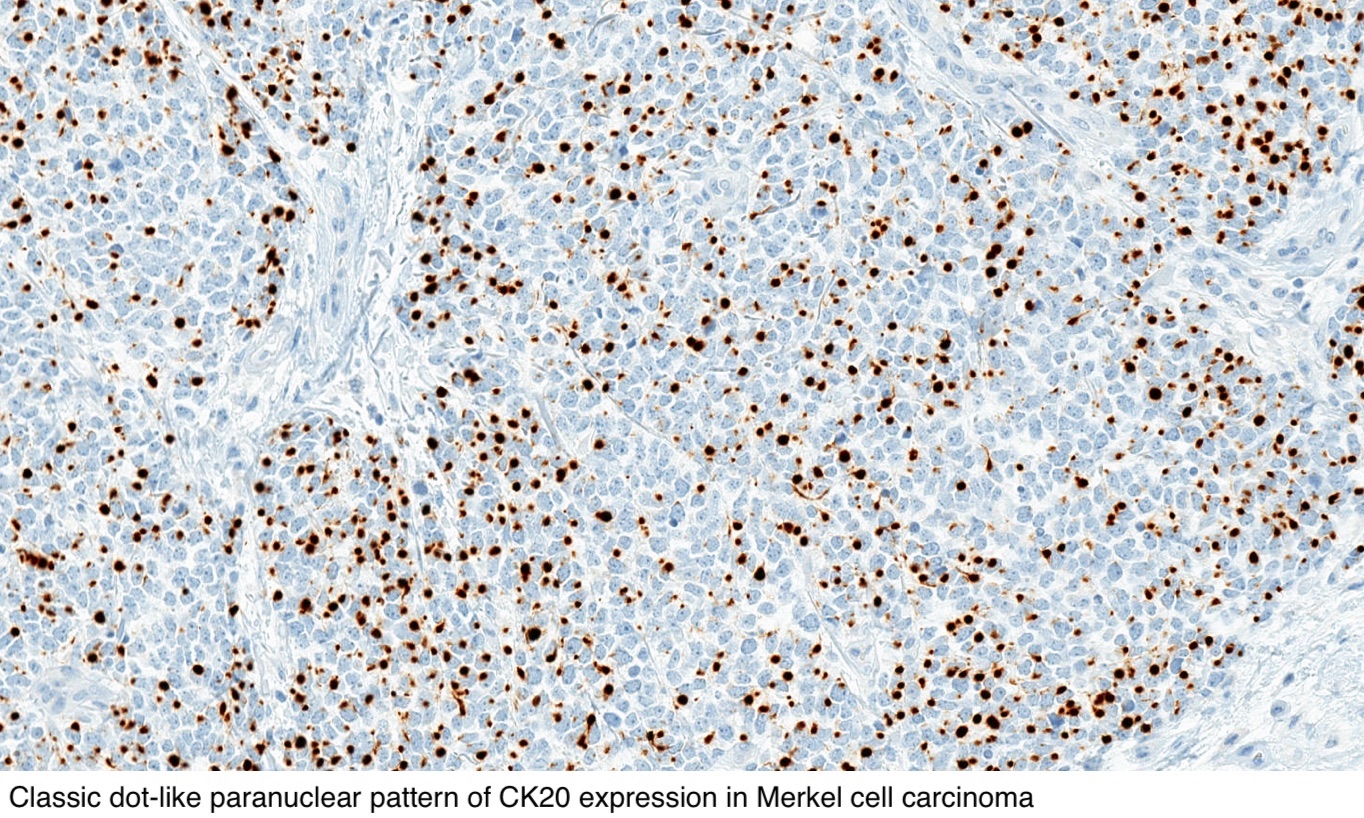
Ck20 Staining Showing The Characteristic Perinuclear Dot Like Positivity Download Scientific Diagram
Pathology Outlines Merkel Cell Carcinoma

Intraepidermal Merkel Cell Carcinoma With Pagetoid Bowen S Disease Miraflor 2016 Journal Of Cutaneous Pathology Wiley Online Library
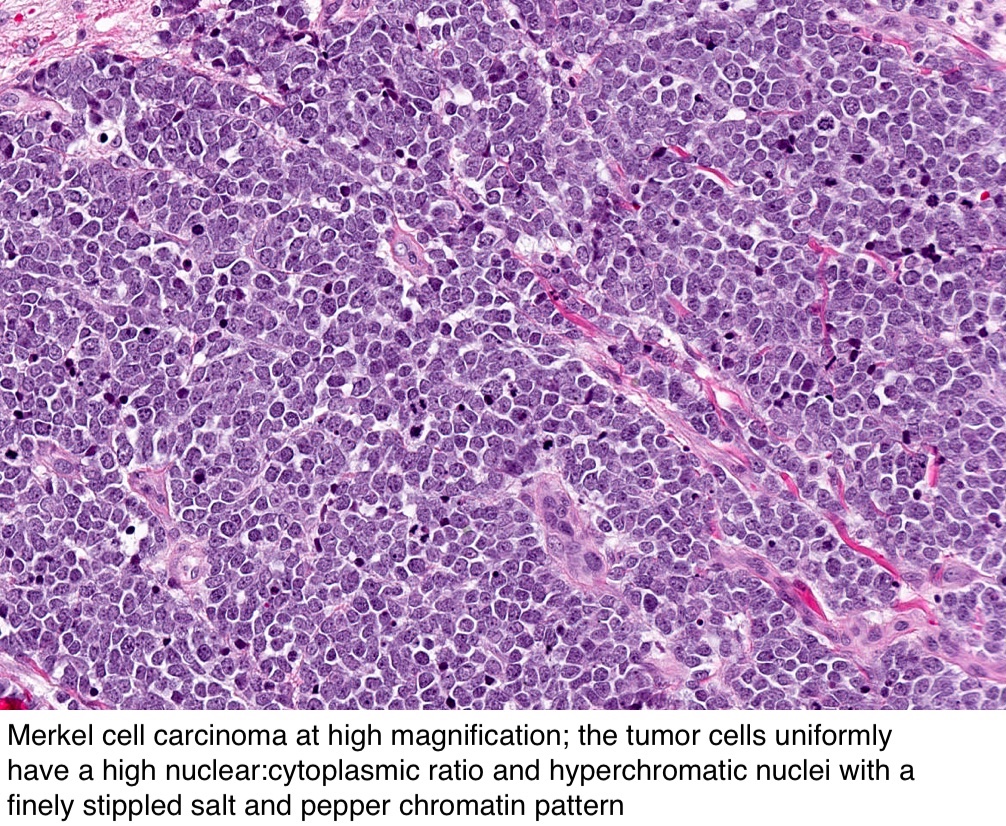
Pathology Outlines Merkel Cell Carcinoma
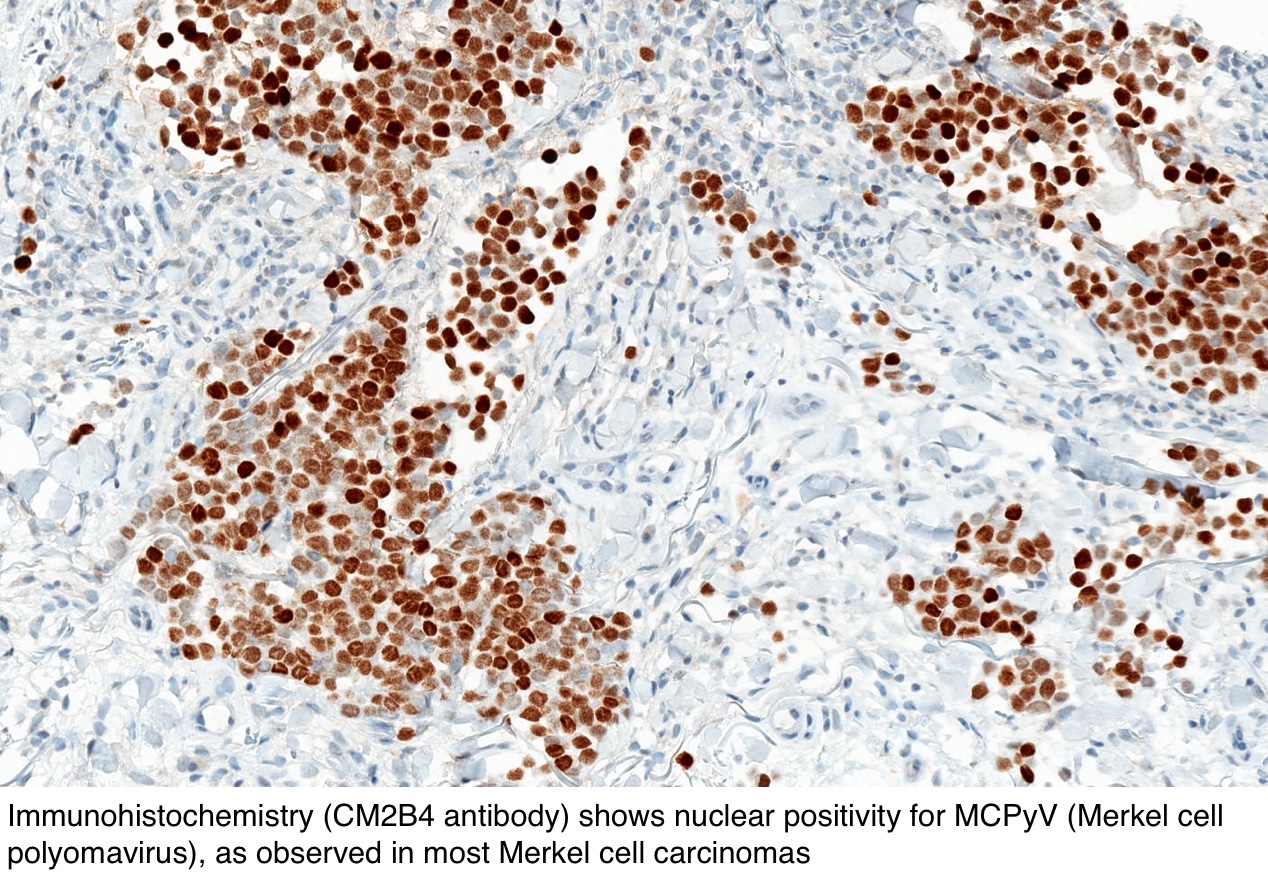
Pathology Outlines Merkel Cell Carcinoma

Researchers Unlock Keys To Staging And Risk Stratification Of Merkel Cell Carcinoma Consult Qd

The Origins Of Various Types Of Skin Cancer 1 Merkel Cell Merkel Cell Download Scientific Diagram

Tumor In Right Thigh Histology Reveals Merkel Cells Carcinoma Download Scientific Diagram